If a company has employees who have worked but have not yet been paid, an adjusting entry is made to record the amount of the unpaid wages as an expense and a liability. Incorrect invoicing can lead to incorrect financial statements. This can happen when invoices are not properly recorded or when estimates are not updated.
What is the Cash Payment Journal? Example, Journal Entries, and Explained
The debit to the loan account, with the principal value, reduces the value of the loan in the Balance Sheet. You are increasing your expenses and decreasing your assets through the amortization process. This allows you to claim your expenses and reduce your taxable income. For example, let’s say a company purchases a patent for $100,000 with an estimated useful life of 10 years and no residual value. In this case, the annual amortization expense would be $10,000 ($100,000 divided by 10). The difference between amortization and depreciation is that depreciation is used on tangible assets.

What are the five main adjusting entries?
The purpose of adjustment entries is to ensure that the financial statements accurately reflect the company’s financial position and performance. Without adjustment entries, the financial statements would not be a reliable source of information for investors, creditors, and other stakeholders. Tangible fixed assets, such as property, plant and equipment, are recorded at cost and are depreciated over a specified useful life. Accumulated depreciation, which is the sum of all depreciation expenses recorded over the life of an asset, is displayed on the balance sheet.
Leveraging AI to address challenges in staffing accountants
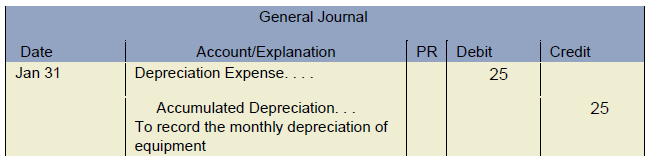
To record prepaid insurance, an adjusting entry is made to decrease the asset account and increase the corresponding expense account. Depreciation expense is the allocation of the cost of a long-term asset over its useful life. To record depreciation expense, an accountant would debit an expense account and credit an accumulated depreciation account. Adjustment entries are an important part of the accounting period and the accounting cycle. The accounting period is the period of time for which financial statements are prepared, usually one year. The accounting cycle is the process of recording, classifying, and summarizing financial transactions for a given accounting period.
- Similarly, it allows them to spread out those balances over a period of time, allowing for revenues to match the related expense.
- Try our payroll software in a free, no-obligation 30-day trial.
- Adjustment entries are crucial in ensuring that financial statements accurately reflect the financial position of a company.
- In addition, the firm debits the cost of any competing patents purchased to ensure the revenue-generating capability of its own patent to the Patents account.
It is important to note that adjustment entries are not recorded in real-time and are typically made at the end of an accounting period. This means that the bookkeeper or accountant must ensure that all adjustment entries are made before financial statements are prepared. Deferrals are revenues or expenses that have been paid or received in advance. To record a deferral, an accountant would debit an asset account and credit a revenue or expense account. The credit entry reflects the accumulated amount of amortization over time. Amortization is similar to depreciation but there are some differences.
What is Amortization Expense?
The five main adjusting entries include the accrual of revenues, accrual of expenses, deferral of revenues, deferral of expenses, and depreciation. The revenue recognition principle requires businesses to recognize revenue when it is earned, regardless of when payment is received. Adjustment entries are necessary to ensure that revenue is recognized in the correct period, even if payment has not been received.
Try our payroll software in a free, no-obligation 30-day trial. Use Form 4562 to claim deductions for amortization and depreciation. The payment is huge and inflated like a balloon, hence the name. A greater portion of earlier payments go toward paying off interest while a greater portion of later payments go toward the principal debt.
This reflects that the asset has been fully expensed and is no longer on the balance sheet. Subtract the residual value of the asset from its original value. If the asset has no residual value, simply divide the initial value by the which journal entry records the amortization of an expense lifespan. There are, however, a few catches that companies need to keep in mind with goodwill amortization. For instance, businesses must check for goodwill impairment, which can be triggered by both internal and external factors.
To avoid this mistake, it is important to keep track of all invoices and ensure that they are recorded accurately. The matching principle is a fundamental accounting principle that requires expenses to be matched with the revenues they generated. Adjustment entries ensure that all expenses and revenues are recorded in the correct period, even if they were not initially recorded. Unearned revenues are revenues that have been received in advance. An example of an unearned revenue would be a deposit for services.
Straight-line amortization is the most common type of amortization, and involves the equal distribution of a loan’s cost over its lifespan. Residual value is the amount the asset will be worth after you’re done using it. The item might not have any value once its lifespan is complete. Another catch is that businesses cannot selectively apply amortization to goodwill arising from just specific acquisitions. The double declining method is an accelerated depreciation method.










